“`html
Essential Guide to an Animal-Based Diet
In recent years, the popularity of an animal-based diet has surged, with many advocating for its numerous health benefits. This essential guide explores the animal-based diet, examining its benefits, protein sources, meal plans, and various related topics to help you make informed choices for optimal health in 2025.
Benefits of Animal-Based Diet
One of the primary advantages of adopting an animal-based diet is the array of nutrients it offers. Animal foods are generally nutrient-dense, providing essential vitamins, minerals, and proteins that are vital for optimal health. Notably, the nutrient density of animal foods surpasses that of many plant-based options. For example, red meat is rich in iron and B vitamins, contributing to energy production and cognitive function. Additionally, animal-derived vitamins such as vitamin B12 are critical, especially for maintaining nerve function and producing red blood cells.
The Role of Animal Protein Sources
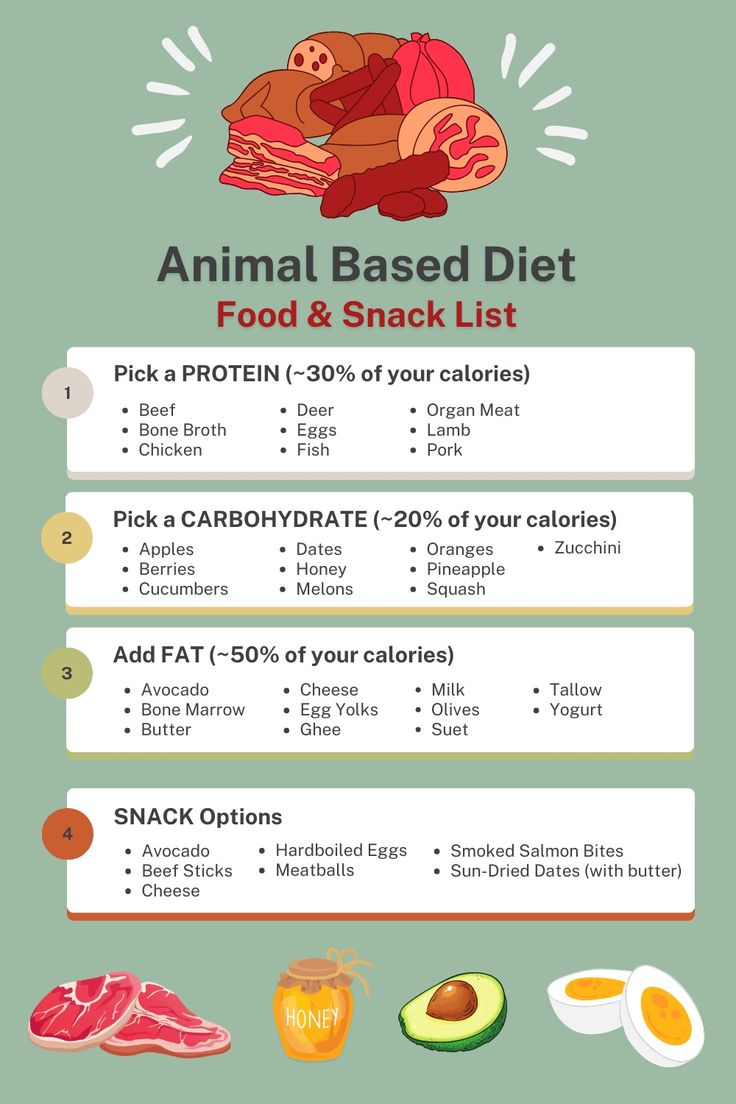
Understanding animal protein sources is crucial for anyone considering this dietary approach. Major sources include beef, chicken, fish, and eggs. Each source offers unique nutritional profiles: beef is an excellent source of iron and zinc, chicken is low in fat and high in protein, fish provides omega-3 fatty acids beneficial for heart health, and eggs supply a complete protein with all nine essential amino acids. These protein-rich animal foods not only fuel muscle recovery after workouts but also support overall health.
Health Risks of Vegetarianism
While vegetarian diets can be healthful, they may pose certain risks related to nutrient deficiencies. Not consuming adequate animal-derived vitamins, such as B12, can lead to serious health issues. Studies indicate that vegetarians might experience lower energy levels and compromised immune function over time. Integrating moderate amounts of animal products can help mitigate these risks and contribute to a more balanced nutritional profile.
Animal-Based Diet and Mental Health
The connection between diet and mental health is increasingly recognized. Animal products offer dietary fats critical for brain health and neurotransmitter function. Research suggests that omega-3 fatty acids, prevalent in wild-caught fish, can improve mood and cognitive performance. Furthermore, regular consumption of nutrient-dense animal foods may lower the risk of conditions such as anxiety and depression, supporting the vital relationship between diets and mental health.
Diverse Animal Protein Sources for Optimal Health
Embracing a variety of animal protein sources is vital for a well-rounded animal-based diet. The inclusion of diverse options not only enhances taste but also ensures a broader spectrum of nutrients. Each protein source has its own benefits and nutritional markers, allowing individuals to tailor their diets to their specific health goals. For example, while beef offers robust iron content, chicken provides lean protein ideal for those focused on muscle gain.
Beef Nutrition and Grass-Fed Benefits
The nutritional profile of beef, particularly grass-fed varieties, has come under the spotlight in recent years. Grass-fed beef advantages include higher levels of omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants, which can play a role in reducing inflammation. Additionally, grass-fed beef is less likely to contain antimicrobial residues and is often associated with sustainable farming practices. Regular consumption of this nutrient-dense meat can support various health aspects, including muscle recovery and metabolic health.
Chicken for Muscle Gain and Performance
When it comes to chicken for muscle gain, this versatile protein source is paramount for athletes and active individuals. Chicken is not only high in protein but also low in fat, making it an ideal choice for building muscle without excessive calorie intake. Incorporating chicken into meals can be done easily through various cooking techniques such as grilling, baking, or even slow cooking to maintain moisture and flavor. As a staple in an animal-based meal plan, it provides the essential nutrients needed for recovery post-exercise.
Fish as a Protein Source
Fish as a protein source presents numerous health benefits. Fish, particularly varieties like salmon and sardines, are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which have been shown to reduce the risk of heart disease and improve cognitive function. Incorporating fish into your diet at least twice a week can significantly enhance your intake of these essential fats, supporting overall health and vitality. Additionally, wild-caught fish typically boast a higher nutrient profile compared to farmed alternatives due to their natural diet and environment.
Creating Your Animal-Based Meal Plans
Developing effective animal-based meal plans is key to successfully integrating this diet into your lifestyle. Meal prepping can streamline the process, ensuring you have nutritious options readily available throughout the week. Establishing a routine for planning your meals not only enhances adherence but also maximizes the health benefits of your animal diet. Aim to include a variety of proteins and side dishes to keep your meals balanced and enjoyable.
Importance of Eggs in Diet
Often called the perfect food, eggs are an excellent component of an animal-based diet. They provide complete proteins, meaning they contain all the essential amino acids necessary for muscle building and recovery. Including eggs in your breakfast or snacks can be incredibly beneficial. Whether boiled, scrambled, or poached, eggs can be easily incorporated into various meals while delivering vitamin D, selenium, and choline—crucial for brain function.
Healthy Dairy Products and Their Benefits
An often-overlooked component of the animal-based diet is dairy, which offers a wealth of health benefits. Incorporating dairy products not only contributes calcium for bone strength but also delivers proteins that support muscle maintenance and recovery. Greek yogurt is an excellent choice, packed with probiotics that enhance gut health and improve digestion, further amplifying the variety of nutrients obtained from dairy products.
Nutritional Value of Different Meats
Keen awareness of the nutritional value of different meats is essential for structuring a balanced animal-based diet. Red meats, while rich in iron, can also be higher in calories. On the other hand, lean meats like turkey and chicken are lower in fat, making them great for weight management. Knowing how to choose meats wisely will aid in balancing your macronutrients while enjoying the spectrum of animal-based foods available.
Tips for Sustainable Animal Farming
As the demand for animal-based diets continues to grow, the importance of sustainable practices in animal farming can’t be overstated. Sustainable animal farming methods focus on reducing environmental impact while ensuring animal welfare. Choosing sustainable animal products, such as grass-fed beef and pasture-raised chicken, can promote ethical sourcing techniques and healthier animal nutrition, aligning your diet with broader ecological considerations.
Ethical Animal Sourcing Techniques
Choosing ethically sourced animal products enables consumers to contribute positively to the environment and society. Researching where your meat comes from can elevate your diet’s ethical dimensions. Additionally, prioritizing local and organic producers ensures that the animals are treated humanely and nourished properly, thus yielding quality products rich in nutrients without harmful additives. Adopting an ethically centered approach fosters conscientious consumption.
Benefits of a Whole Animal Approach
The whole animal approach maximizes nutritional variety and sustainability. By utilizing all parts of the animal, from cuts of meat to offal, you reduce waste and gain access to an array of nutrients. This technique also encourages exploration and creativity in the kitchen, inspiring home cooks to create meals that honor the entire animal and foster a deeper connection to their food sources.
Animal Food Myths and Misconceptions
It’s essential to dispel common myths surrounding animal diets to make informed choices. Misconceptions about the health impacts of consuming animal products often stem from misinformation about saturated fats or protein sources. In actuality, moderate, well-sourced animal product consumption serves as part of a balanced diet and has been linked to various health benefits, including improved muscle recovery and metabolic function. Being well-informed allows for a personalized approach to animal-based dieting.
Key Takeaways
- The animal-based diet is nutrient-dense and can have significant health benefits.
- Diverse animal protein sources are essential for overall health and muscle building.
- Incorporating ethical and sustainable practices into your food choices is crucial.
- Knowledge of cooking methods and meal prep can enhance adherence to your diet.
- Cultivating myths about animal foods will help in making better dietary choices.
FAQ
1. What are the primary benefits of an animal-based diet?
The benefits of an animal-based diet include improved nutrient density, increased protein intake, and enhanced mental health. Animal foods are rich in essential vitamins and minerals that support overall well-being and ability to recover after exercise.
2. Can an animal-based diet support muscle gain?
Absolutely! Consuming sufficient protein from sources such as beef, chicken, and fish can significantly aid in muscle gain and recovery. These animal protein sources deliver essential amino acids necessary for muscle synthesis.
3. How does the consumption of fish benefit health?
Fish as a protein source is particularly beneficial for its high omega-3 fatty acid content, important for heart health and reducing inflammation. Regular fish consumption is associated with numerous health advantages, including improved cognitive functions.
4. Are there health risks associated with being vegetarian?
Yes, excluding animal products can lead to certain nutrient deficiencies, particularly vitamin B12 and iron. These deficiencies can result in fatigue and immune dysfunction if not properly managed.
5. How can one create effective meal plans for an animal-based diet?
To create effective animal-based meal plans, incorporate a variety of protein sources like meat, fish, eggs, and dairy. Meal prepping and maintaining diversity in food choices can enrich your diet and ensure you meet your nutritional needs.
“`